Measuring the Predictability of Radio Signal Strength along Public Transportation Routes
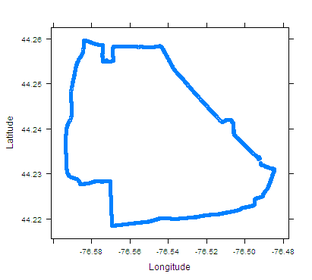 Route of a popular bus route in Kingston, Ontario.
Route of a popular bus route in Kingston, Ontario.
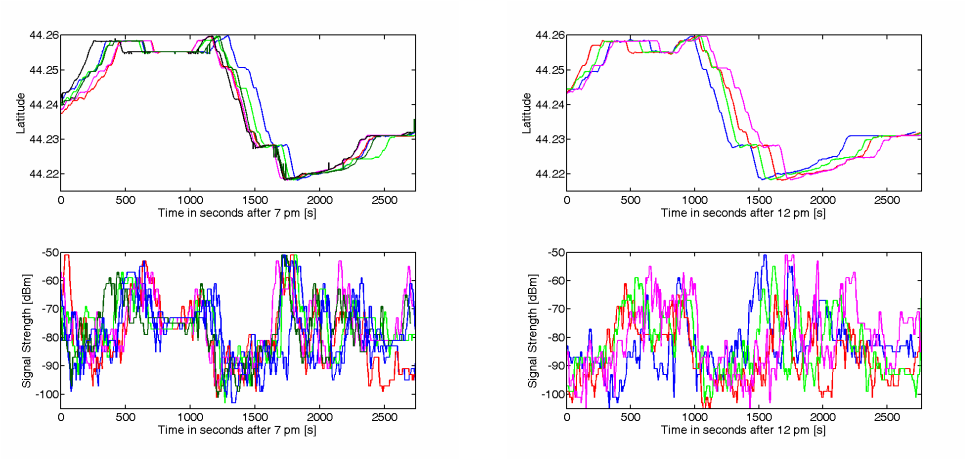
In this project a database of signal strength measurements and GPS coordinates is generated for a popular bus transportation route in Kingston, Ontario (shown to the left), that covers sub-urban and urban neighborhoods. The data will be analyzed to determine:
- Signal strength predictability in different geographical locations and times of the day. Preliminary results indicate that signal strength patterns are repeated along the route (as shown in the measurements below).
- Location predictability of the bus at different times of the day. This is to investigate the effects of traffic lights, and congestion on the prediction accuracy as shown below.
- Correlation between signal strength and received data rate in Mbit/s. Practical models for data rate variability will then be developed for use in robust resource allocation.
Modeling and Simulating Predictive Resource Allocation in LTE Networks using ns-3
 Two level scheduler implemented in the LTE ns-3 module.
Two level scheduler implemented in the LTE ns-3 module.
In this project, we developed a predictive radio access framework (P-RAN) that leverages future data rate predictions and instantaneous rate-opportunistic scheduling. The framework is integrated into the LTE schedulers of the open source Network Simulator 3 (ns-3) LTE module.
We also investigate how signal strength uncertainty can be efficiently modeled. We show that simple asymmetric triangular fuzzy numbers can be used if the Signal to Interference plus Noise Ratio (SINR) exhibits a log-normal prediction error.
A robust resource allocation framework for predictive video streaming that incorporates the fuzzy rates is also proposed. The framework allows the operator to control the desired degree of constraint satisfaction (i.e. ensuring video smoothness) under rate uncertainty. The framework also ‘learns’ the degree of uncertainty through feedback and prediction, via a Kalman Filter and tunes the fuzzy model to reflect the current channel variability.
We also investigate how signal strength uncertainty can be efficiently modeled. We show that simple asymmetric triangular fuzzy numbers can be used if the Signal to Interference plus Noise Ratio (SINR) exhibits a log-normal prediction error.
A robust resource allocation framework for predictive video streaming that incorporates the fuzzy rates is also proposed. The framework allows the operator to control the desired degree of constraint satisfaction (i.e. ensuring video smoothness) under rate uncertainty. The framework also ‘learns’ the degree of uncertainty through feedback and prediction, via a Kalman Filter and tunes the fuzzy model to reflect the current channel variability.
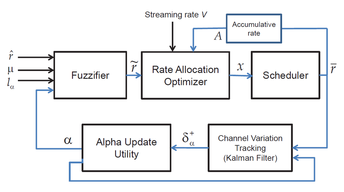 Robust resource allocation with channel variation tracking.
Robust resource allocation with channel variation tracking.
Publications:
- Towards Predictive Radio Access: Modeling, Simulation, and Evaluation in LTE Networks [paper]
H. Abou-zeid, H.S. Hassanein, and R. Atawia
ACM Modeling, Analysis and Simulation of Wireless and Mobile Systems (MSWiM), Sept. 2014, to appear. - Robust Resource Allocation for Predictive Video Streaming Under Channel Uncertainty [paper]
R. Atawia, H. Abou-zeid, H.S. Hassanein and A. Noureldin
IEEE Global Commun. Conf. (GLOBECOM), Dec. 2014, to appear.
Vehicle Mobility Simulation using Open Street Maps and Microscopic Traffic Generation
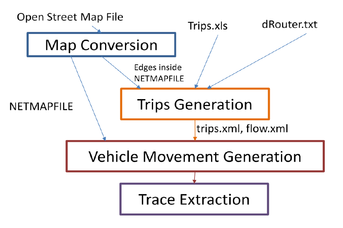 Vehicle Mobility Simulation Process.
Vehicle Mobility Simulation Process.
Muhammad Muhaimin, Hatem Abou-zeid, and Hossam Hassanein
(NSERC URSA and CISC 499 Projects, 2013)
The objective of this project is to develop a tool that generates realistic vehicle mobility traces with minimal knowledge of the underlying map converters and microscopic vehicle simulators. To do so, we integrate
Publications:
(NSERC URSA and CISC 499 Projects, 2013)
The objective of this project is to develop a tool that generates realistic vehicle mobility traces with minimal knowledge of the underlying map converters and microscopic vehicle simulators. To do so, we integrate
- a microscopic vehicle traffic simulation engine SUMO "Simulation of Urban MObility",
- and real world maps from Open Street Maps
Publications: